Structural and functional characterization of orphan proteins
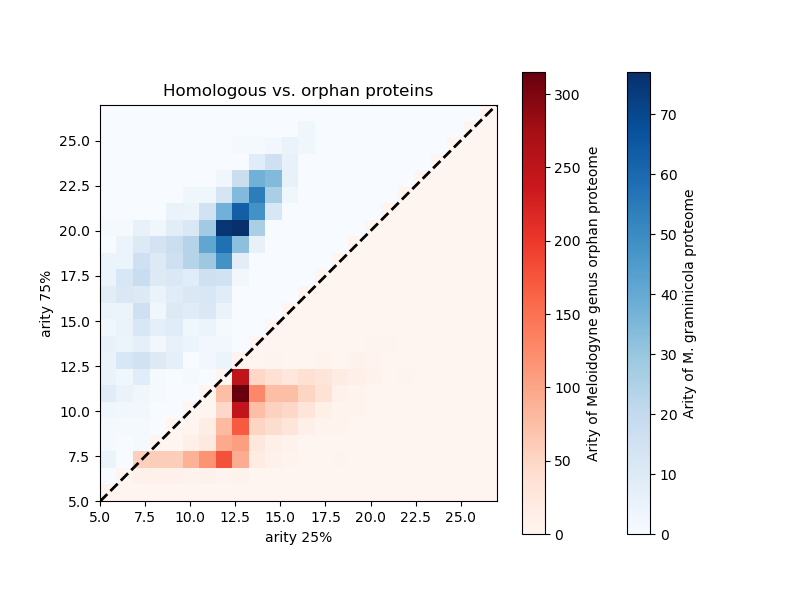
Proteins with no identified homologs (and thus not belonging to any protein family) are called orphans. Orphan proteins are present in every species, spanning from about 5 to 35% of the proteome. “Orphan” is an umbrella definition including unrelated evolutionary events. Orphan proteins can:
- have emerged recently (we talk thus of de novo proteins)
- have diverged considerably from the family they belong (divergent homologs, usually considered as more frequent than de novo proteins)
Orphan proteins pose many unsolved challenges: how can we distinguish de novo and divergent proteins? How can we predict their structure, given that traditional deep learning methods cannot help us predicting homolog-free sequences?
